Strangulation is a life-threatening form of assault that can lead to severe brain damage if not treated promptly. When the neck is compressed, the blood supply to the brain is reduced, causing potential damage from the lack of oxygen. This can result in immediate injuries or long-term neurological deficits. Medical professionals use Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) to assess the extent of brain damage after strangulation. But can MRI detect all types of brain injuries following such incidents?
The question of whether MRI can check for brain damage after strangulation is crucial for both victims and healthcare providers. MRI scans are widely known for their accuracy and detail in detecting abnormalities in brain structures. They are capable of revealing brain damage from a lack of oxygen, assessing old brain injuries, and even detecting nerve damage. However, understanding the specific types of brain injuries MRI can identify is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Importance of Early Detection and Treatment of Brain Damage
Early detection of brain damage is critical to improving patient outcomes after strangulation. Immediate identification of injuries allows healthcare providers to initiate appropriate treatment, which can prevent further complications. Timely intervention can also minimize long-term cognitive impairments and enhance recovery prospects.
MRI is invaluable for early detection, offering detailed images that help identify abnormalities even before symptoms manifest. By understanding the full extent of brain damage, doctors can tailor interventions that target specific issues, such as restoring oxygen flow to the brain or managing traumatic injuries. This proactive approach is vital in minimizing the long-term effects of brain damage, making early MRI evaluation an essential step in the medical response to strangulation cases.
Understanding Strangulation and Its Impact

Strangulation is an alarming form of violence that can have devastating effects on the brain. It occurs when external pressure is applied to the neck, obstructing airflow or blood flow to the brain. This can result in a rapid decrease in oxygen levels, leading to hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), traumatic brain injuries (TBI), and other severe consequences.
The impact of strangulation can be both immediate and long-lasting. In the short term, victims may experience confusion, dizziness, or unconsciousness. Long-term effects can include memory loss, cognitive dysfunction, and psychological issues. Understanding these impacts is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Types of Strangulation
Strangulation can be classified into three main types, each with distinct mechanisms and potential impacts on the brain:
Manual Strangulation
Manual strangulation involves the use of hands to apply pressure to the neck. This type is often seen in cases of domestic violence or assault. The pressure can compress blood vessels and airways, leading to a significant reduction in oxygen supply to the brain. The resulting lack of oxygen can cause immediate brain damage and, if prolonged, lead to irreversible injuries.
Ligature Strangulation
Ligature strangulation occurs when an object, such as a rope or cord, is used to constrict the neck. This method can be particularly dangerous as it often applies constant pressure, further restricting blood flow. The risk of brain damage increases with the duration of the strangulation, leading to potential hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy or other severe brain injuries.
Hanging
Hanging is a form of strangulation where the body’s weight applies pressure to the neck, often cutting off blood flow to the brain entirely. While it may result in immediate loss of consciousness, the long-term effects can be devastating. Survivors may experience traumatic brain injuries, nerve damage, and other neurological deficits due to the lack of oxygen and potential cervical spine injuries.
Physical and Psychological Consequences
Strangulation can lead to various physical and psychological consequences that affect the victim’s overall health. Physically, victims may suffer from neck pain, difficulty breathing, and even visible injuries such as bruising or swelling. These symptoms can be warning signs of more severe underlying issues, such as brain injuries or vascular damage.
Psychologically, the trauma of strangulation can have lasting effects. Victims may experience anxiety, depression, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These psychological impacts can further complicate recovery, making comprehensive medical and psychological support essential for victims.
Potential Brain Injuries
Strangulation can result in several types of brain injuries, each with distinct symptoms and long-term effects:
Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE)
Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) occurs when the brain is deprived of oxygen for an extended period. Strangulation can lead to HIE by cutting off oxygen-rich blood flow to the brain. Symptoms may include confusion, memory loss, and difficulty concentrating. If left untreated, HIE can result in permanent brain damage, affecting cognitive functions and quality of life.
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) can occur when the head is subjected to physical force during strangulation. The impact can cause brain bruising, bleeding, or swelling. Symptoms of TBI vary from mild concussions to severe cognitive impairments, affecting memory, speech, and motor functions. Immediate medical attention is crucial to manage TBIs and prevent further complications.
Stroke or Other Vascular Injuries
Strangulation can also lead to strokes or other vascular injuries due to the abrupt disruption of blood flow. This can result in brain cell death, leading to significant neurological deficits. Symptoms of a stroke include sudden numbness, confusion, and loss of coordination. MRI can detect these injuries early, allowing for timely intervention and reducing the risk of long-term damage.
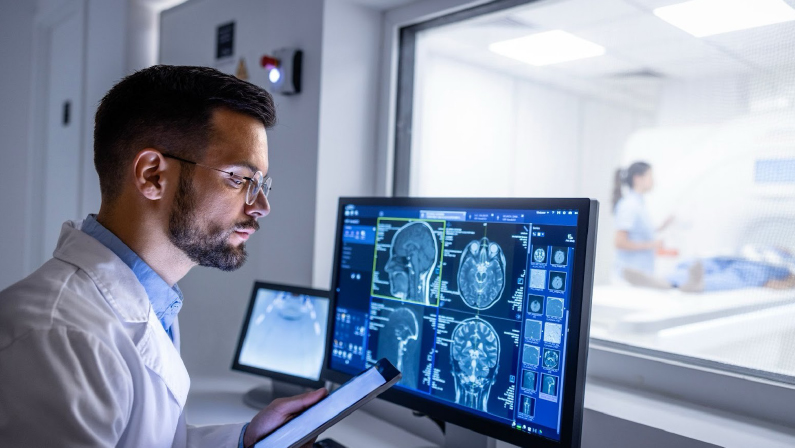
How MRI Works in Detecting Brain Damage
MRI, or Magnetic Resonance Imaging, is a non-invasive imaging technique used to visualize the internal structures of the body, including the brain. It utilizes powerful magnets and radio waves to generate detailed images of the brain’s anatomy, making it a valuable tool in detecting brain damage.
Does an MRI show brain damage? Can MRI detect nerve damage in the brain? In cases of strangulation, MRI can identify abnormalities in brain tissue, detect changes in blood flow, and assess the extent of nerve damage. This ability to visualize the brain in high detail allows healthcare providers to diagnose and treat various forms of brain injuries effectively.
Advantages of MRI in Brain Imaging
MRI offers several advantages in brain imaging, making it an essential tool for diagnosing brain damage:
- High Resolution: MRI provides detailed images of the brain’s structures, allowing for accurate detection of abnormalities.
- Non-Invasive: The procedure is non-invasive and does not involve radiation, making it safe for repeated use.
- Comprehensive Imaging: MRI can assess the entire brain, including blood vessels and soft tissues, providing a comprehensive view of potential injuries.
- Early Detection: MRI can detect brain damage before symptoms become apparent, enabling early intervention and treatment.
- Versatility: MRI can diagnose various brain injuries, from traumatic brain injuries to hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and strokes.
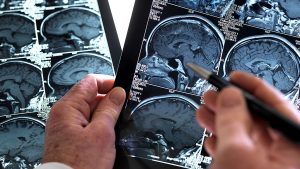
Can MRI show old brain injury?
Yes, an MRI can show old brain injuries. While MRI is often used to diagnose acute brain injuries, its detailed imaging capabilities also make it invaluable for detecting the effects of past trauma or injuries. Here’s how an MRI can reveal old brain injuries, the types of injuries it can identify, and the specific imaging techniques used to do so.
MRI’s Role in Diagnosing Brain Damage After Strangulation

MRI plays a crucial role in diagnosing brain damage after strangulation. By providing detailed images of the brain, MRI allows healthcare providers to identify the specific injuries sustained and determine the best course of treatment.
Detecting Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE)
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) occurs when strangulation restricts blood flow and oxygen supply to the brain. The prolonged lack of oxygen can lead to brain cell death and irreversible damage. Understanding how HIE develops is crucial for prompt diagnosis and intervention.
MRI findings indicative of HIE include changes in brain tissue, such as swelling or lesions. These abnormalities can be detected early, allowing healthcare providers to assess the severity of the damage and implement appropriate treatment strategies.
Identifying Vascular Injuries
What are the signs of strokes or other vascular damage on MRI? MRI can identify signs of strokes or other vascular injuries resulting from strangulation. These signs may include changes in blood vessel structures, areas of reduced blood flow, or hemorrhages. Early detection of vascular injuries through MRI can prevent further complications and improve patient outcomes.
Can an MRI show brain damage from lack of oxygen?
Yes, an MRI can indeed show brain damage caused by a lack of oxygen, a condition known as hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) or cerebral hypoxia. When the brain is deprived of oxygen, it can lead to various types of damage, and MRI is one of the most effective tools for diagnosing and evaluating the extent of this damage.
Importance of Immediate Medical Attention After Strangulation
Immediate medical attention after strangulation is crucial to minimize brain damage and improve recovery prospects. Even if symptoms are not immediately apparent, seeking medical evaluation is essential to identify potential injuries and initiate appropriate treatment.
Prompt MRI scans can provide valuable insights into the extent of brain damage, guiding healthcare providers in implementing targeted interventions. Early intervention can prevent further complications, reduce the risk of long-term cognitive impairments, and enhance the overall recovery process. For rapid and accurate diagnosis, running to One Step Diagnostic should be your first priority. They offer comprehensive MRI scans specifically designed to detect brain damage resulting from strangulation.
The Critical Role of MRI in Detecting Brain Damage
MRI plays a vital role in detecting brain damage after strangulation, offering detailed images that help diagnose various forms of brain injuries. From identifying hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy to assessing vascular damage, MRI provides invaluable insights that guide treatment and improve patient outcomes.
Understanding the capabilities of MRI in detecting brain damage is essential for both victims and healthcare providers. By recognizing the importance of early detection and intervention, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their brain health and ensure a comprehensive medical response after strangulation incidents.
The expert team at One Step Diagnostic is equipped to handle such emergencies, providing detailed imaging and prompt analysis to identify any potential brain injuries. Contact them today!