When it comes to medical imaging, X-rays are a widely recognized tool for visualizing bones and some soft tissues. But can they reveal the presence of blood clots?
This question has often perplexed patients and even some healthcare professionals.
In this article, we’ll discuss the science of X-rays and their limitations when detecting blood clots.
We’ll also explore alternative methods more suitable for identifying these potentially life-threatening obstructions in the circulatory system.
What Are Blood Clots?
Blood clots, also known as thrombi, are gel-like clumps of blood that form in response to injury or in situations when the blood coagulates excessively. They are crucial to the body’s defense mechanism to prevent excessive bleeding when a blood vessel is damaged.
Blood clotting is a complex process involving platelets and clotting factors that work together to seal the injured area and stop bleeding.
However, problems can arise when these clots form inappropriately or fail to dissolve naturally, potentially leading to serious health issues such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), or stroke.
Why It’s Important To Detect Them?

Blood clots can have life-threatening consequences if left undetected and untreated. Detecting them promptly is vital for several reasons:
- Preventing Complications: Identifying and addressing blood clots early can prevent them from growing larger or breaking loose, which could lead to more severe conditions like a pulmonary embolism or stroke.
- Minimizing Tissue Damage: Blood clots can obstruct blood flow, causing tissue damage and pain. Detecting and treating them promptly can minimize the extent of tissue damage.
- Improving Patient Outcomes: Timely detection and intervention improve patient outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term complications associated with blood clots, such as chronic vein insufficiency or post-thrombotic syndrome.
Understanding X-rays

X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation that can penetrate the body, creating detailed images of its internal structures. This technology relies on the differential absorption of X-rays by different tissues within the body, making it a valuable diagnostic tool for a wide range of medical conditions.
How do X-rays work?
X-rays work by emitting a controlled dose of radiation through the body. Dense structures, such as bones, absorb more X-rays and appear white on the X-ray image, while softer tissues, like muscles and organs, allow more X-rays to pass through and appear darker.
This contrast in X-ray absorption enables healthcare professionals to visualize and diagnose various medical issues, from fractures to infections.
Limitations of X-rays
Despite their utility, X-rays have limitations when detecting certain conditions. They are particularly effective at highlighting structural abnormalities but are less adept at revealing subtle changes in soft tissues.
Additionally, X-rays use ionizing radiation, which can be harmful in high doses and may pose risks, especially in pregnant individuals. Furthermore, X-rays cannot provide real-time imaging and are unsuitable for diagnosing dynamic conditions or assessing blood flow.
Can X-rays Detect Blood Clots?
Given the limitations of X-rays in imaging soft tissues and their inability to visualize dynamic processes, they are generally not the primary method for detecting blood clots.
Blood clots do not typically absorb X-rays significantly, making them challenging to detect directly. Instead, other imaging modalities, such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI, are preferred for identifying blood clots in various parts of the body, depending on the suspected location.
These methods offer superior sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing clot-related conditions and are essential tools in the medical evaluation of thrombosis.
Other Diagnostic Techniques for Blood Clots
While X-rays may not be the ideal choice for detecting blood clots due to their limited soft tissue visualization, several other diagnostic methods excel.
These techniques offer a range of options for healthcare professionals to accurately identify and assess blood clots in different body parts, ensuring timely intervention and appropriate treatment.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound often considered the first-line imaging modality for suspected deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or blood clots in peripheral veins, utilizes high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images of blood flow.
By observing blood flow patterns and identifying areas of clot formation, ultrasound provides a non-invasive and highly accurate means of diagnosing DVT. It is particularly valuable for detecting clots in the legs, arms, and other superficial veins.
D-dimer test
The D-dimer test measures the presence of a specific protein fragment in the blood that is released when a blood clot breaks down.
Elevated D-dimer levels can indicate the presence of an active clotting process in the body.
While this test is highly sensitive and useful for ruling out blood clots in certain situations, it is not specific enough to confirm a clot’s exact location or extent. Additional imaging studies are typically required to confirm a diagnosis.
CT scans
Computed tomography (CT) scans utilize a series of X-ray images taken from different angles to create cross-sectional images of the body.
CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) is a specialized form of CT scanning that is particularly effective for diagnosing pulmonary embolism (PE) – a condition caused by lung blood clots.
CTPA can provide detailed information about the location and size of the clot, helping healthcare providers determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
MRI scans
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) employs strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of soft tissues in the body.
While MRI is not the first-choice method for diagnosing blood clots, it can be valuable in certain situations, such as detecting clots in the deep veins of the pelvis.
MRI can offer excellent visualization of blood vessels and surrounding tissues, aiding in diagnosing and managing clot-related conditions.
Venography
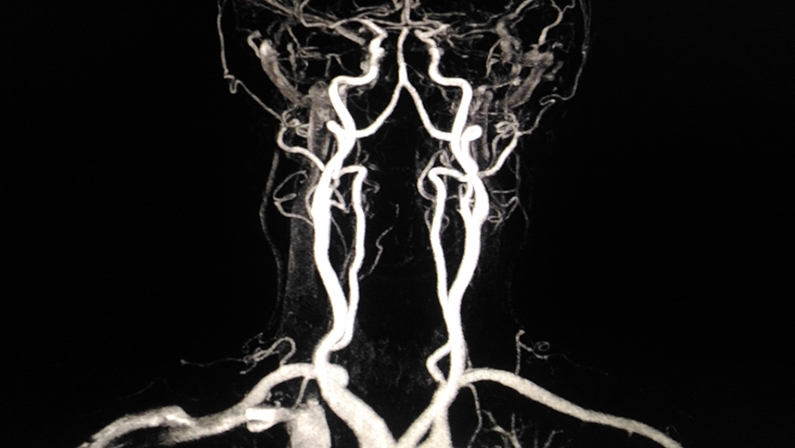
Venography is a less common but highly specialized diagnostic procedure for visualizing blood clots in deep veins. It involves injecting a contrast dye into a large vein, typically in the foot or ankle, followed by X-ray imaging.
Venography can provide precise information about the location and extent of blood clots, making it particularly useful when other imaging methods yield inconclusive results.
However, it is an invasive procedure and is usually reserved for cases where alternative imaging methods have not provided a clear diagnosis.
The Ideal Diagnostic Procedure for Blood Clots
Healthcare providers rely on a range of diagnostic procedures to diagnose blood clots effectively. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach, some methods are considered more ideal based on the specific clinical scenario and the suspected location of the clot.
Here, we explore the attributes that make a diagnostic procedure ideal for detecting blood clots.
- Accuracy and Sensitivity: The ideal diagnostic procedure should offer a high level of accuracy and sensitivity, ensuring that blood clots are reliably detected without unnecessary false positives or negatives. In this regard, techniques like ultrasound and CT scans offer precision in identifying clots’ presence, location, and size.
- Non-Invasiveness: Minimizing patient discomfort and risk is crucial. Non-invasive methods, such as ultrasound and blood tests like the D-dimer, are preferred whenever possible. They allow for rapid diagnosis without invasive procedures, reducing patient stress and recovery time.
- Applicability to Different Clot Locations: Blood clots can occur in various locations throughout the body, from deep veins to the lungs and even the brain. The ideal diagnostic procedure should be versatile enough to assess clots in different anatomical regions. Imaging techniques like CT scans and MRIs can be adapted to various clot-related scenarios, providing comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
Premier Facility for Blood Clot Diagnosis
Selecting the most appropriate diagnostic procedure is paramount. While X-rays have their role in medical imaging, they are not the go-to option for detecting blood clots due to their limitations in visualizing soft tissues.
Instead, healthcare providers rely on a combination of ultrasound, CT scans, MRI scans, and blood tests like the D-dimer to ensure precise and timely diagnoses.
When it comes to premier diagnostic facilities for blood clot detection, One Step Diagnostic is a leader in providing comprehensive, patient-centered care. If you suspect a blood clot or require a thorough evaluation, don’t hesitate to contact us for expert consultation and state-of-the-art diagnostic services.
For unrivaled expertise in blood clot diagnosis and exceptional patient care, visit One Step Diagnostic today at locations in Sugar Land, Houston, The Woodlands, and Dickinson. Your health is our priority, and we’re here to provide you with the highest standard of diagnostic services.
Contact us today and take the first step towards an accurate diagnosis!