Effective medical diagnosis involves imaging methods such as CT scans and MRI.
Both techniques help your doctor analyze your internal body parts through X-ray pictures. Findings from these scans are beneficial for treating and managing your health condition.
But do these procedures vary in function? Find out what’s the difference between a CT scan and an MRI and what they can do for your treatment.
What is the Difference between a CT scan and an MRI?
While both require you to lie on a table while a scanner captures images, they differ in the technologies used and the scope of their purpose.
What does a CT scan show?
A CT scan or Computed Tomography uses radiation to capture quality images of any body parts.
While lying flat on a table, a beam takes cross-sectional pictures of your bones, muscles, fat, organs, and blood vessels.
This procedure typically lasts 10 to 30 minutes and only uses the lowest radiation dose. The quick method allows radiation exposure disappear quickly.
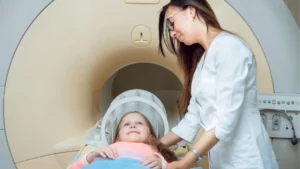
What does an MRI show?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field and radio frequency to show images of your soft tissue, bone and internal structures, and organs.
When your doctor requests an MRI, expect that the procedure requires you to lie on a table that will slide into a tunnel-like machine.
There are other options of open MRI machines that allow you breathing room during the examination.
Another piece of equipment essential for an MRI is the coil. It is wrapped around your body or placed on your shoulder, serving as antenna for the radio frequency pulses.
It helps the machine gather images of a particular part of your body. The procedure may last from 15-90 minutes.
Different types of CT scan
CT scans have different types, depending on a specific condition or body part.
Here are the different types of CT scans your doctor may need you to undergo:
CT angiography
CT angiography is required to diagnose a patient’s risk for heart disease. Using a contrast dye injected into your arteries, the scanner will capture images of your blood flow. Results can evaluate the condition of your blood flow for both the peripheral vascular and coronary systems, which is vital in detecting early signs of heart complications. Aside from heart diseases, the CT scan can see conditions such as aneurysms and atherosclerosis.
CT abdomen scan
Imaging for your abdomen examines your organs, such as the liver, kidneys, pancreas, and spleen.
With specialized equipment, clear images can also gather interpretations of your lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract, colon, and rectum condition. This procedure can show the cause of abdominal pain, such as appendicitis, colon cancer, inflamed colon, abscess, and diverticulitis.
CT bone scan
This diagnostic procedure creates images for your bones. It detects changes and abnormalities in your bones through horizontal or axial images.
Head CT
A CT scan for the head can present images of your skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses. It can diagnose conditions such as birth (congenital) defects of the head or brain, brain, infection, stroke, bleeding in the brain, trauma, and fluid buildup in the brain.
CT scan of chest/lungs
This type of CT scan examines small nodules in the lungs and can explain irregularities such as chest pain, fever, difficulty in breathing, and unexplained cough. It can also be a vital test in diagnosing early-stage lung cancer.
Cardiac CT
A cardiac CT uses specialized technology that is important for physicians in detecting complications in your heart structures, arteries, aorta, and valves.
CT neck
This scanning procedure studies the soft tissues and organs of the neck, including the muscles, tonsils, airways, throat, adenoids, thyroid, and other glands.
Pelvic CT scan
A CT scan in the pelvic area diagnoses tumors and fractures. It can also detect appendicitis and different types of cancers like ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, cervical cancer, and bladder cancer, among others.
CT scan of kidneys
This imaging method helps determine tumors, lesions, kidney stones, fluid and abscesses around your kidneys, and other congenital abnormalities.
CT scan of the spine
A CT scan for the spine assesses the spine for conditions such as tumors, injuries, herniated disks, malformations, and structural anomalies.
Different types of MRI
MRI does not use radiation. It also produces more specific, detailed, and accurate images compared to CT scans.
Functional MRI (fMRI)
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) identifies small changes in blood flow caused by brain activity. It can evaluate the effects of stroke and provide insights for handling treatment and management of critical brain injuries that are undetectable in other types of imaging procedure.
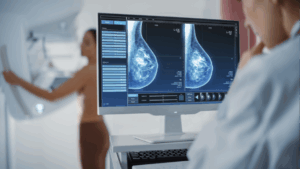
Breast scans
Breast scans are best done alongside mammography and breast ultrasound to detect breast complications such as cancer. This type of MRI detects small breast lesions that may have been missed in other breast procedures.
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
This type of MRI looks into the activities of the blood vessels and finds out if there are complications that need to be addressed. Blood vessels from critical areas such as the brain, neck, and chest are studied with images that help detect conditions such as atherosclerosis and aneurysms.
Magnetic resonance venography (MRV)
Using magnetic resonance technology and contrast dye, an MRV can spot complications in body organs, specifically caused by leg pain other than vein problems.
Cardiac MRI
A cardiac MRI uses large magnets and radio frequencies to diagnose complications in the heart’s anatomy. It accurately detects coronary heart disease, cardiovascular diseases, and congenital heart disease.
What are the advantages of a CT scan?
CT scan is a common choice in evaluating diseases and injuries. It provides a generalized image of your body part and can be more convenient and affordable.
This imaging technique can:
- Diagnose muscle disorders, infections, and fractures
- Identify tumors
- Assess internal injuries
- Monitor efficacy of treatments like cancer and heart disease
- Evaluating lung and chest problems
- Imaging for patients with metal devices
What are the advantages of MRI?
MRI has the same advantages with CT scans and can perform better with clearer scans.
This procedure allows you to have:
- Detailed and more precise images of organs, soft tissues, and internal structures
- Comparison of normal and abnormal tissues
- Procedure without radiation
What are some disadvantages of each imaging method?
While the imaging method can be an effective solution in diagnosing diseases, it still has disadvantages. However, your physician can still decide to proceed with the procedure significantly if the benefits outweigh the drawbacks.
- Risk for developing cancer. The ionizing radiation from CT scans has a slight risk for cancer.
- Discomfort during the procedure. MRIs take longer than CT scans and require over 20 to 40 minutes in a closed space. Additionally, it may not be a suitable method for people with claustrophobia. The procedure will also be noisy, but there is a provision for ear protection.
- Require injection. Both imaging techniques require contrast dye injected into you before the procedure.
How do doctors decide which imaging a person should receive?
The use of CT scans and MRI can be similar. But your doctor will decide which type of procedure is appropriate for you, based on several factors, including:
- Medical reason
- Required details for the images
- Conditions such as pregnancy
- Phobia and tolerance to discomfort
Who Should Not Have an MRI?
MRI scans have low-risk levels but are not recommendable for everyone.
Here are the signs that MRI is not for you:
- Claustrophobic
- Intolerance to noise from the machine
Moreover, if you have metallic implants in your body, you may receive reactions that may cause you pain and discomfort.
Talk to your health provider if you have any of the following:
- An IUD
- A pacemaker
- Shrapnel
- Eye implants
- Aneurysm clips
- Orthopedic hardware
- Artificial joints
- Dark tattoos
Who Should Not Have a CT Scan?
Since CT scans use ionizing radiation, it can build up in your life, which is a risk of developing cancer.
Aside from this, you also need to talk to your doctor if you are:
- Pregnant
- Allergic reaction to dyes
CT scan and MRI specialists in Texas
Although you already know the difference between a CT scan and MRI, it is up to your healthcare provider what specific procedure you should undergo.
While CT scans tend to be a common first choice for imaging, there are cases when your physician shall require an MRI to detect diseases that may not show during your first imaging test.
Your doctor is the one who will recommend the most effective method to detect any abnormalities in your body accurately.
If you are advised to undergo any of these tests, call One Step Diagnostic, an accredited radiology center in Texas with locations in Houston, Sugar Land, Dickinson, and The Woodlands.
We take pride in our state-of-the-art imaging facilities that can perform accurate X-rays for any part of your body with fast and reliable diagnostic results.
Our board-certified radiologists are experts in conducting CT scans, MRIs, and other diagnostic services that you may need for your treatment.
Call us today to book a schedule.