How long does a meniscus tear take to heal? Is one of the most frequently asked questions people ask after their diagnosis. Unfortunately, the answer is not simply because various factors can affect how long it takes for an injury to heal.
However, this article will guide you in determining the real-time healing of the different conditions of a meniscus tear.
What is the Meniscus?
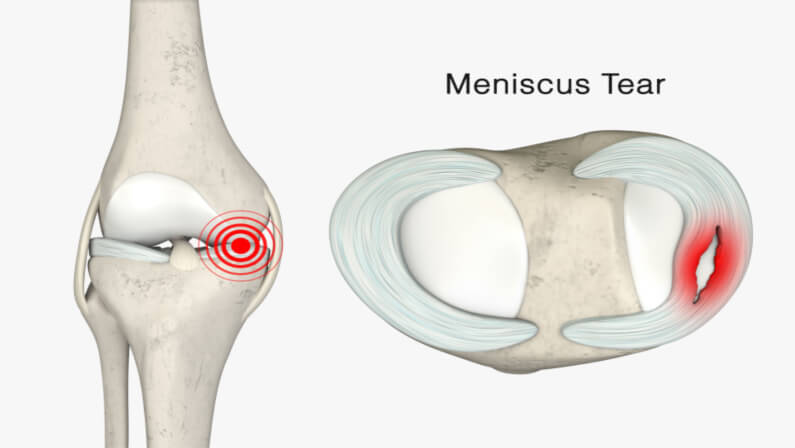
The meniscus, a C-shaped piece of cartilage, is located in the knee joint between the thigh bone and the shinbone. It serves as a cushion, aids in weight distribution, and lessens friction within the joint.
Additionally, it aids in preventing deterioration of the articular cartilage on the ends of the bones. Each knee has two menisci, one on the medial (inside) and one on the lateral (outside) joint.
What Does the Meniscus Do?
The meniscus has a variety of uses due to its size and shape. It contributes significantly to the knee joint’s stability and cushioning.
Specifically, the meniscus serves to:
- Absorb shock. When you walk, run, or leap, the meniscus helps to evenly distribute the weight and stress applied to the knee joint. This lessens the possibility of harm to the joint and injury.
- Improve joint stability. The meniscus prevents the bones from rubbing against one another, stabilizing the knee joint. This lessens the chance of dislocation or other types of harm.
- Lubricate the joint. The meniscus also helps to lubricate the knee joint, which reduces friction and allows for smooth movement.
- Protect articular cartilage. The meniscus acts as a shock absorber, protecting the articular cartilage on the ends of the bones from wear and tear.
How Long Does it Take to Recover from Meniscus Tear Surgery?
Depending on the patient’s age, general health, the extent of the tear, and the type of surgery, the recovery period following meniscus tear surgery may differ.
However, the average healing period for people is four to six weeks. For the first few days following surgery, patients commonly wear crutches and braces to take the weight off the injured knee and prevent further injury.
Within a few days of surgery, physical therapy is frequently started to aid in the recovery of range of motion, strength, and flexibility.
Physical therapy’s primary goals are to treat swelling, avoid the development of scar tissue, and reestablish normal gait patterns and knee motion.
Will a Meniscus Tear Heal on its Own?
Due to its limited blood supply, the meniscus has a limited capacity for self-healing. The meniscus only has blood vessels in the outer third necessary for healing.
The inner two-thirds of the meniscus, which are avascular (without a blood supply) and are referred to as the “white zone,” are affected by most meniscus rips that do not heal on their own.
What is a Meniscus Tear?
A meniscus tear is a frequent knee injury when the meniscus, a C-shaped piece of cartilage in the knee joint, is hurt or torn. An abrupt twisting or bending of the knee joint can cause a meniscus tear, as can general wear and tear over time.
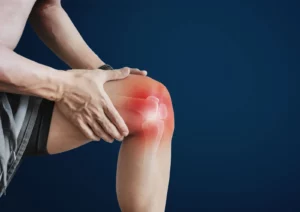
What are the Symptoms of a Meniscus Tear?
Depending on the size and location of the meniscus tear, the symptoms can vary.
The following are some typical signs of a meniscus tear:
- Pain. The first sign of a meniscus tear is typically pain. The knee joint line may be painful, and the discomfort may worsen with motion or when pressure is given to the region.
- Swelling. Inflammation and fluid accumulation in the knee joint after a meniscus tear may cause swelling.
- Stiffness. Due to the knee joint’s restricted range of motion, stiffness may develop.
- Moving the knee with difficulty. A person may have trouble moving the knee joint depending on the location and extent of the tear. During movement, the knee may potentially lock or give way.
What Causes a Meniscus Tear?
Numerous things, such as an immediate traumatic injury or gradual degenerative changes to the knee joint, might result in a meniscus tear.
Meniscus tears have a variety of frequent causes, such as:
Traumatic tears
Traumatic tears in the meniscus are common among athletes who play sports like football, basketball, and soccer.
However, they can happen during any activity that requires knee twisting. Less frequently, lifting while repeatedly kneeling or rising from a squatting position can cause a tear.
Degenerative (atraumatic) tears
Degenerative or atraumatic rips are typically found in older populations and are brought on by biology, meniscal structural disintegration, and degeneration.
Degenerative tears may have been accelerated by knee twisting in individuals.
However, a degenerative tear has a very different pattern than a catastrophic one. This is crucial because a traumatic tear may require a different course of treatment than a degenerative tear.
How is a Meniscus Tear Diagnosed?
A meniscus tear is diagnosed using a combination of physical examination and imaging tests. One Step Diagnostic serving the Houston-area community, offers the imaging tests you’ll need.
X-ray
Your orthopedist will complete a health history and knee examination if a meniscal tear is suspected. They may also request X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to confirm the diagnosis and further assess the knee joint.
MRI
An MRI is a diagnostic method that creates comprehensive images of the body’s organs and structures using a combination of huge magnets, radiofrequency technology, and a computer. It can frequently identify injury or disease in an adjacent ligament or muscle.
Ultrasound
An ultrasound takes visuals of the inside of the body using sound waves. You can find out if you have any loose cartilage that might be caught in your knee by doing this.
Arthroscopy
A tiny cut or incision is created near the knee during arthroscopy. A small, flexible fiber-optic instrument called an arthroscope can be placed via the incision. It has a tiny camera and light.
Medical equipment can be transferred through the arthroscope or further incisions in your knee.
Your doctor might advise arthroscopy to examine your knee if these methods fail to identify the source of your knee pain. Your doctor will also probably use an arthroscope if you need surgery.
Physical Examination
The McMurray test is one of the primary examinations for meniscus injuries. Your doctor will flex your knee before being straightened and rotated. A meniscus tear is put under stress by this.
This movement may ache, click, or make the joint feel cumbersome if you have a torn meniscus.
What Type of Doctor Treats Meniscus Tears?
It is crucial to be seen by a physiatrist, primary care sports medicine physician, or orthopedic surgeon with expertise in sports medicine if you suspect a meniscus tear.
Can You Still Walk with a Torn Meniscus?
After a meniscus tear, simple walking and other activities that don’t include twisting, pivoting, sharp turns of direction, etc., are typically tolerated well.
Tears can worsen with time, but this happens gradually and with many variations. There will typically be additional signs of discomfort if a tear worsens.
What Happens if you Leave a Torn Meniscus Untreated?
The signs of a torn meniscus could linger or even get worse over time if left untreated. Degenerative knee arthritis is more likely to develop in people with progressive meniscus loss.
It’s crucial to acquire a diagnosis and start therapy as soon as possible.
A minor rip could occasionally get well by itself with rest and time. However, larger or more serious tears can necessitate medical attention, including physical therapy, medicine, or surgery.
If you believe you may have a torn meniscus, you should immediately consult a doctor to assist in stopping further injury and help your knee return to normal.
What is the Treatment for a Torn Meniscus?
The severity and location of the meniscus tear, the patient’s general health, and the amount of activity all influence the course of treatment.
Nonsurgical options
RICE (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) may be adequate to ease pain and reduce swelling in cases of small tears. Physical therapy treatment may also be advised to increase the range of motion and strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee.
What is the Surgery for a Torn Meniscus?
Surgery can be required for more serious tears. The surgery for a torn meniscus typically involves arthroscopic surgery.
Arthroscopic Meniscal Surgery
In arthroscopic surgery, a tiny camera is placed into the knee joint to enable the surgeon to either repair or remove the torn meniscus fragment.
To recover knee strength and flexibility after surgery, rehabilitation is frequently required.
This may involve resting and changing one’s activities to allow the knee to heal properly, in addition to physical therapy exercises.
Anti-inflammatory medicines and medications for pain control may also be recommended.
It is important to consult a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for a torn meniscus, as leaving it untreated can lead to further complications and chronic pain.
Tips to Prevent Meniscus Tears
You can wear protective equipment or a brace to support your knee during sports or other activities that could raise your risk of injury.
By routinely engaging in leg-strengthening activities, you can prevent meniscus tears. Your knee joint will be stabilized. As a result, keeping it safe from harm.
Don’t Ignore a Torn Meniscus
In conclusion, a meniscus tear might heal at a different pace based on several variables. While less severe tears that don’t require surgery may recover totally in a few weeks to months, more serious injuries that do require surgery may take longer.
To decide the best course of therapy for a meniscus tear and to create a recovery plan, it is crucial to speak with a healthcare professional and undergo diagnostic imaging.
The most recent imaging tests are available at One Step Diagnostic. With five centers in Houston and additional locations in Sugar Land, Dickinson, and The Woodlands, we have several locations around Texas.