Did you know that early detection of tumors can dramatically improve survival rates, with some cancers showing up to a 90% increase in survival when caught early? Imaging tests are critical for identifying tumors before symptoms arise, enabling timely intervention and better treatment outcomes.
So what is the best imaging test for tumors?
Among the various imaging techniques available, MRI for tumor detection is considered one of the most reliable and precise options. But what sets it apart from other scans? How does MRI detect cancer, and what should you expect from the process? Let’s talk about it.
Why MRI is a Preferred Imaging Method for Diagnosing Tumors
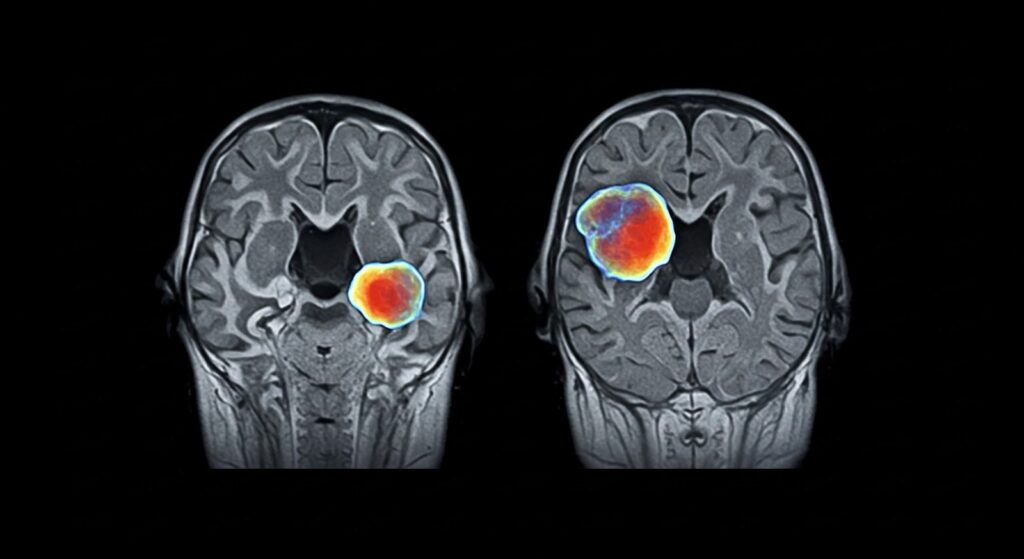
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a preferred method for diagnosing tumors because of its ability to provide highly detailed images of soft tissues without using radiation. Unlike CT scans or X-rays, MRI relies on powerful magnets and radio waves to generate cross-sectional images of the body. Because MRI offers superior soft tissue contrast, it can often detect abnormalities that other imaging methods might miss. This makes MRI an excellent option for detecting tumors in areas like the brain, spine, breast, and abdomen.
How MRI Works for Tumor Detection
MRI creates detailed images of internal structures by using strong magnetic fields and radiofrequency waves. In some cases, doctors use MRI contrast for tumor detection, where a special dye is injected to enhance the visibility of abnormal tissues. This contrast material makes it easier to distinguish between normal and cancerous tissue, helping radiologists detect even the smallest tumors.
Identifying Tumor Location, Size, and Shape
One of the biggest advantages of an MRI scan for cancer diagnosis is its precision in locating tumors. Whether a tumor is deep within the brain or nestled between organs, MRI can map out its exact position, size, and shape, which is critical for treatment planning.
Distinguishing Between Benign and Malignant Tumors
Not all tumors are cancerous, and MRI helps differentiate between benign and malignant tumors. This is done by analyzing tissue density, shape, and contrast uptake. MRI vs. CT scan for tumors often shows MRI is more effective in distinguishing between the two, reducing the need for unnecessary biopsies.
Detecting Early-Stage Tumors
Early detection significantly improves survival rates and treatment success. MRI tumor detection is particularly effective for spotting small, early-stage tumors that might be missed by other imaging methods. This is especially crucial for aggressive cancers that spread quickly.
Monitoring Tumor Growth and Treatment Response
For patients undergoing cancer treatment, MRI scans play a vital role in tracking tumor progression and evaluating the effectiveness of treatments. Unlike CT scans, which involve radiation, MRI can be used repeatedly for long-term monitoring.
Types of Tumors Detected by MRI
MRI can identify tumors in various parts of the body, making it an essential tool in cancer diagnostics.
Brain Tumors
MRI is the gold standard for detecting brain tumors due to its ability to capture highly detailed images of the brain’s structure. It helps doctors assess tumor size, location, and whether it’s affecting surrounding tissues.
Spinal Tumors
Spinal tumors can be difficult to detect, but MRI excels in visualizing abnormalities along the spinal cord, nerves, and vertebrae. This helps neurosurgeons determine the best approach for treatment.
Breast Tumors
While mammograms are commonly used for breast cancer screening, MRI is often recommended for high-risk patients or for evaluating suspicious findings. MRI vs. PET scan for tumors in the breast shows MRI provides clearer soft tissue contrast, which helps in assessing tumor aggressiveness.
Abdominal & Pelvic Tumors
MRI is frequently used to detect tumors in the liver, kidneys, pancreas, and reproductive organs. Since it provides excellent soft tissue visualization, MRI is ideal for identifying cancers in these areas.
Bone & Soft Tissue Tumors
MRI is often the preferred imaging technique for detecting bone and soft tissue tumors, as it provides superior contrast between different tissue types. This makes it particularly useful for diagnosing sarcomas and other musculoskeletal tumors.
MRI vs. Other Imaging Techniques for Tumor Detection
Each imaging method has its strengths, but MRI offers unique advantages in tumor detection.
MRI vs. CT Scan
MRI vs. CT scan for tumors is a common comparison. While CT scans are faster and better for detecting bone abnormalities, MRI provides superior soft tissue contrast and is better for identifying brain, spinal, and muscle tumors.
MRI vs. PET Scan
MRI vs. PET scan for tumors differs in their approach. PET scans highlight metabolic activity, making them useful for detecting cancer spread, while MRI focuses on anatomical details. In many cases, the two scans are used together for comprehensive diagnostics.
MRI vs. X-Ray & Ultrasound
X-rays and ultrasounds are useful for preliminary screenings but lack the detail necessary for tumor detection. MRI, in contrast, offers a high-resolution view that allows for precise diagnosis.
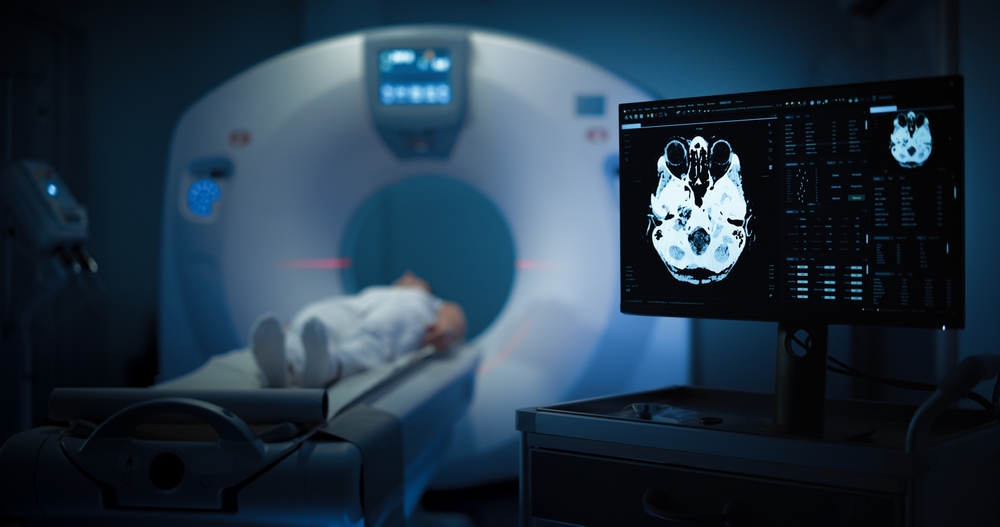
What to Expect During an MRI Scan
If you’re preparing for an MRI scan, here’s a step-by-step overview of the process:
- Preparation
You may be asked to avoid eating or drinking for a few hours before the scan. Remove all metal objects, as they can interfere with the magnetic field.
- Positioning
You’ll lie down on a table that slides into the MRI machine. Depending on the area being scanned, you may be positioned head-first or feet-first.
- Scanning
The machine will produce loud knocking noises as it captures images. You’ll need to remain still to ensure clear images. Earplugs or headphones are often provided to minimize discomfort from the noise.
- Contrast Injection (if needed)
For some scans, a contrast agent will be injected to enhance image clarity.
- Completion
The scan typically takes 30-60 minutes. Afterward, a radiologist will review the images and provide a detailed report.
Benefits of MRI for Tumor Detection
MRI offers multiple advantages when it comes to cancer diagnosis and monitoring. Here are some of the benefits of MRI for cancer screening:
High-Resolution Imaging for Accurate Diagnosis
MRI provides incredibly detailed images, allowing doctors to see even the smallest tumors. This accuracy leads to better treatment planning.
No Radiation Exposure, Making It Safer for Frequent Monitoring
Unlike CT scans and X-rays, MRI does not expose patients to ionizing radiation, making it a safer choice for repeated imaging.
Superior Soft Tissue Contrast for Early Tumor Detection
MRI excels in distinguishing between normal and abnormal soft tissues, improving the chances of detecting tumors early.
Non-Invasive and Painless Diagnostic Method
MRI is a completely non-invasive test with no pain involved, making it a comfortable option for patients.

Where to Get an MRI Scan for Cancer Diagnosis
If you need an MRI scan for cancer diagnosis, One Step Diagnostic offers state-of-the-art imaging services with advanced technology and expert radiologists. Visit One Step Diagnostic or schedule an appointment at our contact page.
MRI tumor detection plays a vital role in early cancer diagnosis and treatment planning. If you suspect any symptoms, don’t wait—schedule your MRI scan today!