Before the advent of nuclear medicine, doctors often require surgery to diagnose interior ailments. But thanks to nuclear medicine scans, is now easier to know how effective treatment works after diagnosis and treatment begin.
Before the advent of nuclear medicine, doctors often require surgery to diagnose interior ailments. But thanks to nuclear medicine scans, is now easier to know how effective treatment works after diagnosis and treatment begin.
They also provide light on various psychiatric, neurological, and addiction-related issues.
Additionally, nuclear medicine uses targeted molecular ultrasound and magnetic resonance sonography, which are beneficial in detecting various types of cancer and outlining blood flow.
Information regarding this cutting-edge medical technology and how it might benefit patients will be covered in this article.
What Is Nuclear Medicine?
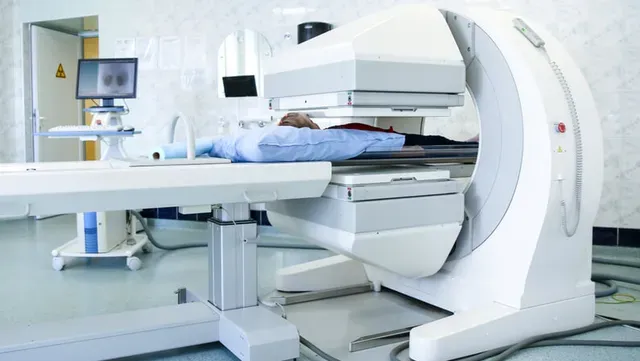
Nuclear medicine scans produce images of organs and body parts that are not visible to the naked eye with conventional X-ray technology.
Before the procedure, you’ll be given an injection of radioactive substances to help radiologists see the activity in your organs using a device called a gamma camera.
Your doctor will be able to make more precise diagnoses of your health issues with the help of the data gathered from nuclear imaging.
If you are diagnosed with a disease, you may need more testing or a customized treatment plan based on your ailment’s specific nature and individual needs.
Why You Might Need One
In the case of cancer, nuclear medicine scans are particularly valuable since they can detect tumors and follow how far they have spread.
They can also be used to assess the efficacy of treatment. It should be noted that there are some limitations to the scans. A scan, for example, may reveal spots that are suspicious of malignancy.
If you get a nuclear scan, your doctor will need to take more detailed images of those locations and examine smaller tumors that may not be shown on the scan.
A biopsy, in which a doctor removes a small bit of a tumor to be examined under a microscope, may be necessary to determine with certainty whether cancer has developed.
Cancer isn’t the only medical disease that can benefit from nuclear medicine scans. Other conditions that it can detect include:
- Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and other neurological conditions
- Problems with the gonads and hormones
- Injuries to the digestive system.
- Cardiac infarction
What To Expect And How It Works
In most cases, you may not need to change your clothes. Once in the scanning area, you will be placed on a table that glides into the scanner, and you will have to lie down.
The scanner will approach you during the procedure. You must remain calm and relaxed. Throughout the procedure, the technologists will keep in close contact with you.

Types Of Scans
These are some of the most popular nuclear medicine scans:
- Thyroid Scan and Uptake – This procedure examines how well the thyroid gland works by evaluating the amount of iodine the thyroid takes i.
- SPECT Liver Scan -To eliminate the possibility of a benign liver tumor, this test is frequently performed as an additional imaging study after a CT, MRI, or ultrasound (hemangioma).
- SPECT brain scan – This two-part test shows how blood flows to tissues and organs.
- Renal Scan – For this test, the kidneys’ blood flow and level of function are assessed.
- MUGA Scan – Patients undergoing chemotherapy often have this test performed to determine how well their hearts are working.
- Meckel’s scan – It is performed for diagnosing Meckel’s diverticulum
- Liver or Spleen Scan -This test determines the liver and spleen’s size and function.
- Hepatobiliary scan -This procedure examines gallbladder function and the bile ducts.
- Gastrointestinal Reflux Study – Also known as an endoscopy, this test examines reflux (liquid moving backward from the stomach into the esophagus)
- Gastric Emptying – This test measures the ability of the stomach to empty itself.
- Gallium Scan – Infection or tumor detection are the primary goals of this test.
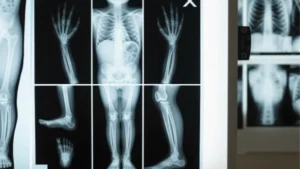
- Bone or Joint Scan – This test determines if there are any abnormalities in the bones or joints
How Long Is A Nuclear Scan?
While the average scanning duration is 45 minutes, the amount of time spent at the hospital depends on the specific treatment and preparations.
Do I Need To Prepare For A Nuclear Scan?
There are different ways to prepare for different types of nuclear medicine exams. Here are a few general pointers:
- Before your scan, you can eat and drink as usual. Nothing particular is required of you to prepare.
- Before the scan, you’ll need to remove any jewelry or other metal objects. You may have to put on a hospital gown at this point.
- Take a bismuth-containing over-the-counter medicine (such as Pepto-Bismol)

Risks And Benefits
Risks
- After the procedure, you may emit a small amount of radiation. Thus, it is important to take precautionary measures to avoid exposing others to it.
- More time and radiation are required for some types of scans. These may cause swelling and hair loss.
- Radiation exposures are typically higher than those associated with standard imaging modalities such as x-rays or computed tomography scans. The odds of developing cancer in the future are thus slightly increased.
Benefits
- It can be used in targeted treatments for pain-alleviation, tumor size reduction, and eliminating malignant cells
- Describes how organs, tissues, and cells work
Consult With The Pros
Nuclear medicine scans are safe if you know the benefits and drawbacks of doing one. Set up an appointment with a board-certified radiologist from One Step Diagnostics if you’re seeking nuclear medicine scan in the Houston, Texas, area.
They would be able to discuss the risks and benefits of each type of nuclear scan with you.