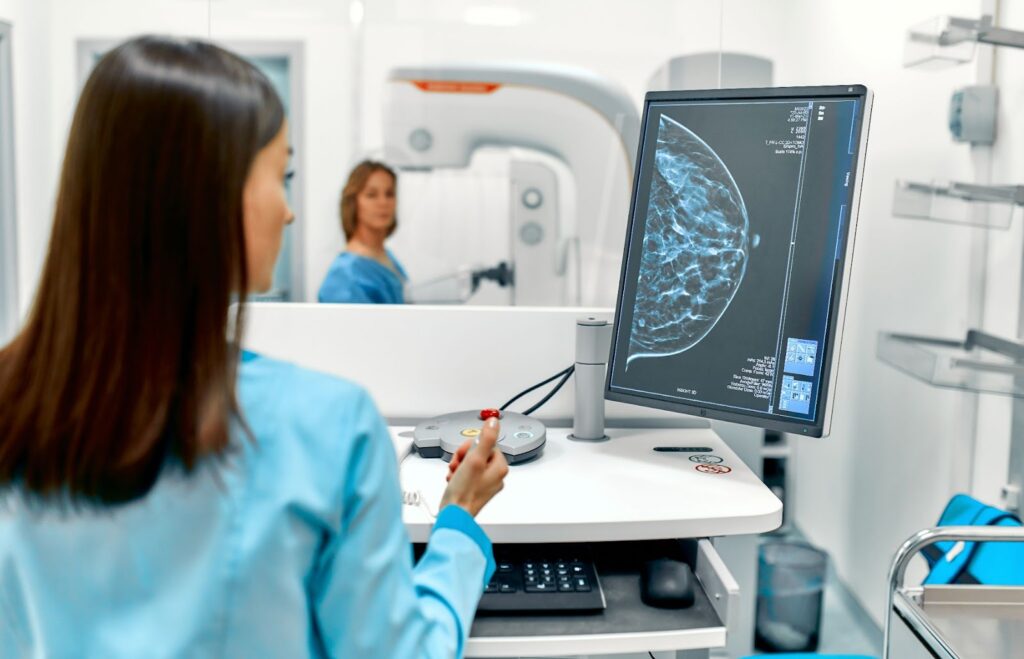
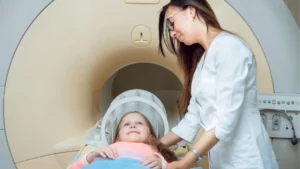
Mammography is an essential tool in the early detection and diagnosis of breast cancer. By providing detailed images of breast tissue, mammograms enable healthcare professionals to identify potential concerns before they become palpable or symptomatic.
In this article, we will explore the significance of mammography in breast cancer detection, explain how it works, and identify common visual indicators of breast cancer visible on mammograms.
Importance of Mammography in Breast Cancer Detection
Early detection of breast cancer significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and survival. Mammography is currently the most effective screening method for identifying early-stage breast cancer, often detecting changes in breast tissue well before physical symptoms develop. Regular mammograms can lead to early intervention, thereby reducing the severity of treatment and improving outcomes for patients.
Understanding Mammography
Mammography is a specialized medical imaging technique that uses low-dose X-rays to visualize the internal structure of the breast. The primary purpose is to detect abnormalities in breast tissue that may indicate the presence of cancer or other breast conditions.
Types of Mammography
2D Mammograms
Also known as conventional mammography, 2D mammograms capture two-dimensional images of the breast from different angles. They are effective for detecting most breast abnormalities, although overlapping tissue can sometimes obscure findings.
3D Mammograms
Also called digital breast tomosynthesis, 3D mammograms create a three-dimensional image of the breast by taking multiple X-ray pictures from varied angles. This type provides a more detailed view of the breast tissue, improving the detection of abnormalities and reducing the likelihood of false positives.
How Mammograms Work
During a mammogram, the breast is compressed between two plates to spread the tissue and allow for clearer X-ray images. The compression might cause some discomfort, but it is crucial for obtaining high-quality images. The resulting images are examined by radiologists who look for unusual areas that might require further investigation.

Visual Indicators of Breast Cancer on a Mammogram
Masses
Masses can appear as dense, white spots on a mammogram. They may be benign (like cysts or fibroadenomas) or malignant. The shape, margins, and density of a mass can provide clues about its nature, with irregular, spiculated (star-like), or ill-defined borders often raising concern for malignancy.
Calcifications
Calcifications are tiny deposits of calcium within the breast tissue that show up as bright white spots on a mammogram. They are categorized as macrocalcifications (larger and usually non-cancerous) or microcalcifications (smaller and sometimes associated with cancer).
Suspicious patterns of microcalcifications can be an early indication of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), a non-invasive form of breast cancer.
Distortions
Distortions in the normal architecture of the breast tissue can suggest the presence of a malignancy. These distortions might appear as areas where the tissue seems pulled or twisted, often caused by the tension exerted by a tumor within the breast.
Asymmetries
Asymmetries refer to areas of the breast that appear different from the same regions in the opposite breast. While some asymmetries are due to natural variations, significant differences, especially when associated with other suspicious findings, may indicate the presence of breast cancer.
Understanding these visual indicators is critical for interpreting mammograms and ensuring early diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer. Regular mammograms and awareness of how breast cancer can present help in the timely and effective management of this disease.

Diagnostic Process Following Mammography
Following a mammography, if any abnormalities or suspicious areas are detected, a series of additional diagnostic steps are typically undertaken to determine whether these findings are benign or malignant. This section will delve into the Bi-RADS scoring system, which helps classify mammogram results, and the additional diagnostic tests that may follow.
Bi-RADS Scoring System
The Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (Bi-RADS) is a standardized scoring system established by the American College of Radiology to categorize mammographic findings. These categories range from 0 to 6, helping radiologists and healthcare providers communicate findings and determine follow-up actions:
- 0: Incomplete – Additional imaging evaluation needed
- 1: Negative – No significant findings
- 2: Benign (non-cancerous) findings
- 3: Probably benign – Short-term follow-up suggested
- 4: Suspicious abnormality – Biopsy should be considered
- 5: Highly suggestive of malignancy – Appropriate action should be taken
- 6: Known biopsy-proven malignancy – In confirmation or further evaluation stages
Additional Diagnostic Tests
If your mammogram results fall into categories that require further investigation, your doctor may recommend a variety of additional diagnostic tests. These tests provide different types of imaging or tissue samples to obtain a clearer understanding of the findings.
Diagnostic Mammogram
A diagnostic mammogram is a follow-up to a screening mammogram that provides more detailed images of specific areas of concern. This targeted approach helps to further evaluate suspicious findings and distinguish between benign and malignant conditions.
Breast Ultrasound
Breast ultrasound uses sound waves to produce images of breast tissues. This non-invasive test is particularly useful for distinguishing between solid masses and fluid-filled cysts, aiding in the accurate diagnosis of breast abnormalities.
Breast MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
A breast MRI utilizes strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the breast. This technique is highly sensitive and is often used in combination with other imaging tests to provide comprehensive insight, especially in women with a high risk of breast cancer.
Biopsy
If imaging tests suggest that an area might be cancerous, a biopsy is performed to remove a sample of breast tissue or cells for laboratory analysis. Various biopsy methods include fine-needle aspiration, core needle biopsy, and surgical biopsy, each chosen based on the characteristics and location of the abnormality.

Ensuring Comprehensive Breast Cancer Diagnosis with One Step Diagnostic
At One Step Diagnostic, we prioritize accurate and thorough diagnostic services to ensure the best possible outcomes for our patients. Utilizing cutting-edge technology and expert medical interpretation, we provide a comprehensive range of diagnostic tests, including advanced mammography, ultrasound, MRI, and biopsy services. Trust One Step Diagnostic for reliable, patient-centered care every step of the way.
Embrace Early Detection and Comprehensive Diagnostic Care
Early detection and comprehensive diagnostic evaluation are vital in the effective management and treatment of breast cancer. Regular mammograms and awareness of potential indicators play a crucial role in identifying abnormalities early. Should further investigation be necessary, understanding the additional diagnostic steps ensures that you are well-prepared to navigate the path toward a precise diagnosis and timely treatment. At One Step Diagnostic, our commitment to excellence in breast health guides you through every step of this crucial journey.